Eigenfunctions and reduced density¶
: .. _Eigenfunctions and reduced density:
The computed eigenfunctions can be printed out into a sperate file (checkpoint). This option can be enabled via the section Checkpoint:
Checkpoint
density save
eigenvectors save
Filename xxxxx
End
The keywords eigenvectors save are to stitch the corresponding checkpointing on.
The eigenfunction-checkpoints consist of two files, eigen_vectors.chk and eigen_vib.chk. The file eigen_vib.chk
contains the vibrational part of the basis set in the grid representation in the following format (example):
1 0.000000 1 0 A1Sigma+
0.124132175316E-13
-0.952336606315E-14
0.982508543282E-14
......
where the each basis function is given in a block. The first line specifies the sate (number, energy, electronic state and vibrational quantum number) followed by the grid values.
The file eigen_vectors.chk contains the expansion coefficients of the eigenfunction in terms
of the Duo ro-vibronic basis set functions using the following format (example):
Molecule = Ca-40 O-16
masses = 39.962590600000 15.994914630000
Nroots = 10
Nbasis = 50
Nestates = 5
Npoints = 501
range = 1.0000000 4.0000000
X1Sigma+, Ap1Pi, a3Pi, b3Sigma+, A1Sigma+, <- States
| # | J | p | Coeff. | St vib Lambda Sigma Omega ivib|
1 0.0 0 0.999999782551E+00 1 1 0 0.0 0.0 0
.....
Here the first eight lines represent a signature of the spectroscopic model (atoms, masses, specification of the basis),
the line 9 is a header followed by the records with the eigen-coefficients and corresponding quantum numbers and labels using the
following format: running number within the 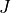 ,parity(p)-block
,parity(p)-block 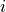 ,
, 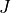 ,
, 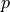 ,
the coefficient
,
the coefficient 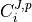 , State,
, State,  ,
, 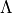 ,
, 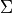 and vibrational basis set number
(a combined number representing the contracted vibrational basis set function from for all electronic states combined).
and vibrational basis set number
(a combined number representing the contracted vibrational basis set function from for all electronic states combined).
The optional keyword Filename (alias Vector-Filename) is to change the checkpoint-prefix eigen
to filename. The default name is eigen_vectors.chk.
The option density save is to compute the vibrational reduced density for all eigenfuncitons on a grid of bond length points, computed as follows
![\rho_(r) = \sum_{v,v'} \sum_{{\rm State},\Lambda,\Sigma} [C_{v,{\rm State},\Lambda,\Sigma}^{i}]^* C_{v',{\rm State},\Lambda,\Sigma}^i \phi_{v}(r)^* \phi_{v'}(r) \Delta r](_images/math/69027157f67aec111ed78e18353b526288385e03.png)
Writing the wave functions to disk¶
Both the vibrational (J=0, uncoupled) basis functions and the coefficients of the expansion of the final (J>0 and coupled) wave functions can be written to disk by including in the Duo input a section with the following structure:
checkpoint
eigenfunc save
filename CO
end
Two files will be produced, called in our example CO_vib.chk and CO_vectors.chk.
The file CO_vib.chk contains the values of the vibrational basis functions at the grid points
and has the following structure:
1 0.000000 1 0 A_1Sigma+
0.417251193034E-06
0.913182486541E-06
0.140429031525E-05
0.191466765349E-05
0.243955552609E-05
0.298913870277E-05
0.356440215967E-05
0.417282770822E-05
0.481737299860E-05
0.550475969611E-05
0.623909577848E-05
The first line describes the assignment of the vibrational basis function; the first number is a counter over all
vibrational wave functions; the second is the energy in cm-1; the third is the state quantum
number indicating the electronic state; the fourth is the  vibrational quantum number; finally, the label of the
electronic state is reported. What follows is the value of the vibrational wave function at the grid points.
The file ends with the line
vibrational quantum number; finally, the label of the
electronic state is reported. What follows is the value of the vibrational wave function at the grid points.
The file ends with the line
End of contracted basis
The file CO_vectors.chk contains the values of the expansion coefficients of the final wave functions.
The structure is as follows:
Molecule = C-12 O-16
masses = 12.000000000000 15.994914504752
Nroots = 3
Nbasis = 0
Nestates = 1
Npoints = 100
range = 0.6500000 3.0000000
Morse_ <- States
| # | J | p | Coeff. | St vib Lambda Sigma Omega|
1 0.0 1 0.100000000000E+01 1 1 0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 2 0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 3 0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 1 0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 1 0.100000000000E+01 1 2 0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 3 0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 1 0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 1 0.000000000000E+00 1 2 0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 1 0.100000000000E+01 1 3 0 0.0 0.0
End of eigenvector
The first seven lines are a header containing the names of the atoms, the atomic masses, the number of wave functions
computed, the total dimension of the 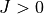 or coupled Hamiltonian matrix,
the number of electronic states in the calculations, the number of grid points and range of the grid (in AA).
The numbers following are:
or coupled Hamiltonian matrix,
the number of electronic states in the calculations, the number of grid points and range of the grid (in AA).
The numbers following are: # is a counter over the rovibronic wave functions; J is the total [2]
The density checkpoint file has the following structure:
0.545190480438E-08 || 1.5 0 1
0.286121234769E-07 || 1.5 0 1
0.134835397210E-06 || 1.5 0 1
0.572802754694E-06 || 1.5 0 1
0.220181930274E-05 || 1.5 0 1
0.768598025530E-05 || 1.5 0 1
0.244490197607E-04 || 1.5 0 1
Where the first column represent the reduced density value on a grid point 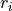 , followed by a dilemeter
, followed by a dilemeter ||, 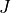 , parity
, parity 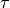 and the state number as in the Duo output.
and the state number as in the Duo output.
Footnotes