Nuclear hyperfine structure¶
Provided nuclear hyperfine interaction curves, Duo calculates field-free hyperfine structure of diatomic molecules. Currently, Duo supports cases where one of the nuclei possess nuclear spin, e.g., 14N16O and 24MgH. Nuclear electric quadrupole interaction and nuclear magnetic dipole interactions including Fermi-contact, nuclear spin-electron spin dipole-dipole, nuclear spin-orbit, nuclear spin-rotation, can be involved in the calculation. The hyperfine calculation is turn on with the following section:
hyperfine
I 1
end
where the value after the keyword I indicates the nuclear spin.
Two output files are generated after calculation.
The one named hyperfine.states contains nuclear hyperfine resolved states.
The columns in this file are:
1. counting number, 2. energy [cm-1], 3. total degeneracy,
4. 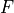 , 5.
, 5. 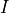 ,
6. parity, 7.
,
6. parity, 7. 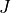 , 8. state, 9.
, 8. state, 9.  ,
10.
,
10. 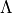 , 11.
, 11. 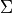 ,
12.
,
12. 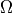 , respectively.
, respectively.
The other named hyperfine.trans contains the hyperfine transitions.
This file has five columns which are:
1.counting number of the upper state,
2.counting number of the lower state,
3.Einstein-A coefficient,
4.transition wavenumber [cm-1],
5.line strength.
Line strengths in this file are calculated by
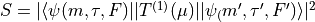
where 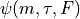 and
and 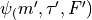 are the wavefunctions
of the hyperfine states.
are the wavefunctions
of the hyperfine states. 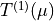 is the tensor of transition
electric dipole moment.
Line strengths have the unit of
is the tensor of transition
electric dipole moment.
Line strengths have the unit of 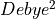 .
.
An electric dipole moment curve should be defined in a dipole section in the first place.
dipole 1 1
name "<X,2Pi|DMC|X,2Pi>"
spin 0.5 0.5
lambda 1 1
factor 1 (0, 1 or i)
type polynom
values
A0 1
end
You may turn off the hyperfine calculation by:
hyperfine none
I 1
end
The global setup of J,
jrot 0.5 - 3.5
affects the maximum of F.
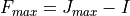 .
The minimum of
.
The minimum of F is always 0 or 1/2.
Currently, Duo does not support refinement of hyperfine curves.
Thus, fitting and hyperfine sections cannot be activated simultaneously.
The nuclear hyperfine interaction curves are introduced with the following seven key words:
hfcc-a, hfcc-bF, hfcc-c, hfcc-d, hfcc-ci, hfcc-eqq0 and hfcc-eqq2.
The default units are angstrom and cm-1.
Hyperfine couplings between electronic states are not allowed at present.
hfcc-a¶
Nuclear spin - orbit interaction curve is defined by an hfcc-a section.
This term is important when the electron orbital angular momentum is non-zero.
hfcc-a 1 1
name "<X2Pi|NSO|X2Pi>" (Nuclear spin-orbit)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-bF¶
The Fermi-contact interaction curve 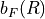 is defined by an
is defined by an hfcc-bF section.
This term is important when the electron spin angular momentum is non-zero.
hfcc-bf 1 1
name "<X2Pi|FC|X2Pi>" (Fermi-contact)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
factor 1
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-c and hfcc-d¶
The electron spin - nuclear spin dipole-dipole
interaction curves 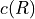 and
and 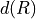 are defined by
are defined by hfcc-c and hfcc-d sections.
The 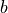 constant defined by Frosch and Foley can be
calculated by
constant defined by Frosch and Foley can be
calculated by
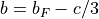 .
.
hfcc-c 1 1
name "<X2Pi|SDND_C|X2Pi>" (Electron spin - nuclear spin dipole-dipole, c)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-d 1 1
name "<X2Pi|SDND_D|X2Pi>" (Electron spin - nuclear spin dipole-dipole, d)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-eqq0 and hfcc-eqq2¶
The nuclear electric quadrupole
interaction curves 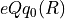 and
and 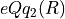 are defined by
are defined by hfcc-eqq0 and hfcc-eqq2 sections.
These terms are active when
the nuclear spin is not less than 1.
hfcc-eqq0 1 1
name "<X2Pi|eQq0|X2Pi>" (Electric quadrupole eQq0)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-eqq2 1 1
name "<X2Pi|eQq2|X2Pi>" (Electric quadrupole eQq2)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end
hfcc-ci¶
The nuclear spin - rotation curve 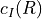 is defined by an
is defined by an hfcc-ci section.
This term is usually negligible compared with other nuclear hyperfine interactions.
Nevertheless,
when all the other hyperfine couplings are inactive,
this term becomes important, e.g.
for a 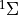 state of a nuclear spin 1/2 molecule.
state of a nuclear spin 1/2 molecule.
hfcc-ci 1 1
name "<X2Pi|NSR|X2Pi>" (Nuclear spin - rotation)
spin 0.5
factor 1.0
type polynom
values
A0 0.1
end